This Day, That Year – March 16
Thu 16 Mar 2023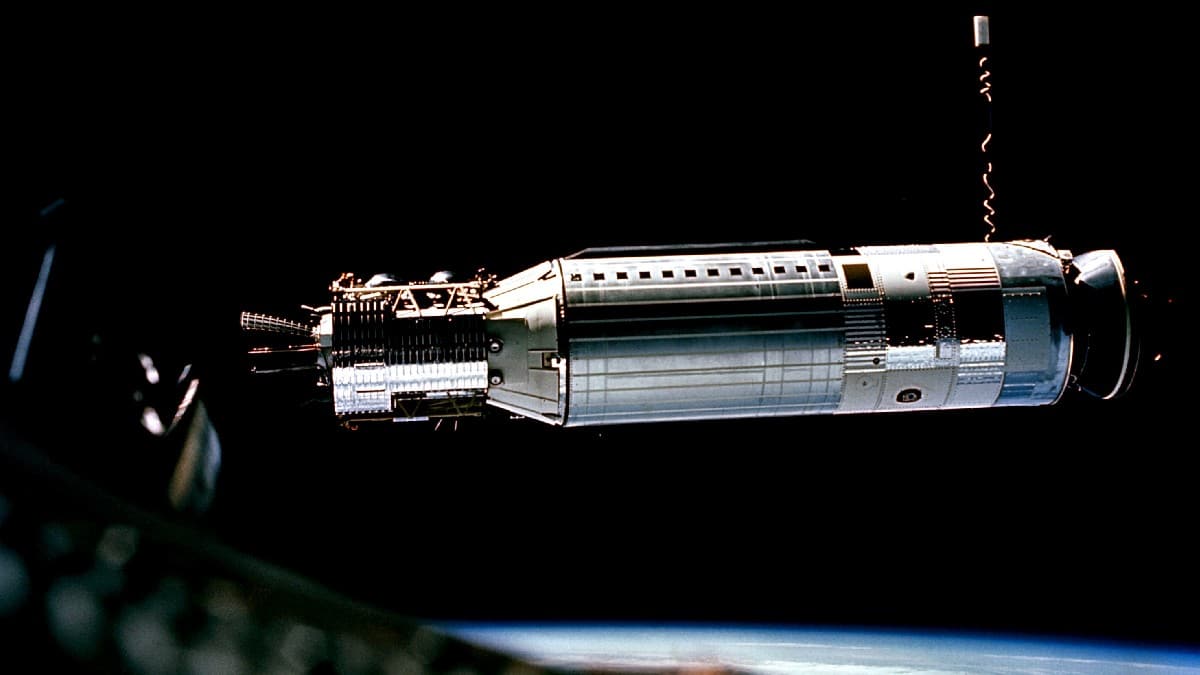
This day in history we feature the Gemini 8. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and David Scott launched the spacecraft on this day in 1966.
Trivia – Gemini 8
Gemini 8 (officially Gemini VIII) was the sixth crewed spaceflight in NASA’s Gemini program. It was the 14th crewed American flight and the 22nd crewed spaceflight overall. The mission conducted the first docking of two spacecraft in orbit, but also suffered the first critical in-space system failure of a U.S. spacecraft which threatened the lives of the astronauts and required an immediate abort of the mission. The crew returned to Earth safely. Flown by pilot David Scott and command pilot Neil Armstrong, the flight marked the second time a U.S. civilian flew into space and the first time a U.S. civilian flew into orbit.
Related read – Astronaut trio touch back to Earth after half-a-year amid stars
Gemini VIII was planned to be a three-day mission. After being launched into an 87-by-146-nautical-mile orbit, on the fourth revolution it was to rendezvous and dock with an Agena target vehicle, which had been earlier launched into a 161-nautical-mile circular orbit. This was to be the first space docking in history. Four separate dockings were planned. During the first docking, Pilot David Scott planned to perform an ambitious, two-hour-and-10-minute extra-vehicular activity (EVA), which would have been the first since Ed White’s June 1965 spacewalk on Gemini IV. On a 25-foot tether for one and a half revolutions around the Earth, Scott would have retrieved a nuclear emulsion radiation experiment from the front of the Gemini’s spacecraft adapter, then activate a micrometeoroid experiment on the Agena. Then he was to move back to the Gemini and test a minimum-reaction power tool by loosening and tightening bolts on a work panel. During the EVA, after Armstrong undocked from the Agena, Scott was to don and test an Extravehicular Support Pack (ESP) stored at the back of the spacecraft adapter. This was a backpack with a self-contained oxygen supply, extra Freon propellant for his Hand Held Maneuvering Unit, and a 75-foot extension to his tether. He would practice several maneuvers in formation with the Gemini and Agena vehicles (separated at distances up to 60 feet), in concert with Armstrong in the Gemini. The flight also carried an additional three scientific, four technological, and one medical experiment.
Source – Wikipedia

 Apr 20 2024
Apr 20 2024












